The cost of a fiber laser system will greatly vary depending on your applications. than fiber lasers, CO. lasers experience higher levels of variation in the quality and output of the laser. Fiber lasers are significantly faster at cutting thin sheets (< 8 mm) than CO, lasers, particularly when cutting stainless steel. The key variables when deciding between a CO2 and fiber laser are: Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. 5 mm stainless steel cutting sample HD Plasma, 10 mm stainless steel cutting sample CO2, 10 mm stainless steel cutting sample Fiber, 10 mm stainless steel cutting sample HD Plasma, 15 mm stainless steel cutting sample CO2, 15 mm stainless steel cutting sample Fiber, 15 mm stainless steel cutting sample HD Plasma, 5 mm mild steel cutting sample HD Plasma, 10 mm mild steel cutting sample HD Plasma, 15 mm mild steel cutting sample HD Plasma. Interlocks stop the laser from firing if the laser is no longer fully enclosed i.e. marking laser machine fiber stylecnc co2 between flying manual user glass difference many know metal 

 High power CO2 lasers (above 6kW) are less common than higher powered fiber lasers. The price for CO2 laser marking systems usually ranges between $35,000 and $80,000. CO2 Lasers however gain an edge when it comes to material types and the flexibility to adapt to a wider range of materials.
High power CO2 lasers (above 6kW) are less common than higher powered fiber lasers. The price for CO2 laser marking systems usually ranges between $35,000 and $80,000. CO2 Lasers however gain an edge when it comes to material types and the flexibility to adapt to a wider range of materials.  Regular maintenance of all machine components (laser system, chiller, extraction unit and machine) is essential to prevent costly servicing and also to prevent machine downtime. A CO, The smaller wavelength of a fiber laser means it is not within the absorption range of non-metallic materials (i.e.
Regular maintenance of all machine components (laser system, chiller, extraction unit and machine) is essential to prevent costly servicing and also to prevent machine downtime. A CO, The smaller wavelength of a fiber laser means it is not within the absorption range of non-metallic materials (i.e.  Refer to BS EN 60825-1 (IEC 60825-1) for precise definitions of laser classes and indications on the limits of accessible radiation. Known Technology/Comfort Level: If you are currently running one or more CO2 laser systems inyour facility you're likely to sway very heavily in that technology direction initially as it is thedemon you know vs. the one you do not.
Refer to BS EN 60825-1 (IEC 60825-1) for precise definitions of laser classes and indications on the limits of accessible radiation. Known Technology/Comfort Level: If you are currently running one or more CO2 laser systems inyour facility you're likely to sway very heavily in that technology direction initially as it is thedemon you know vs. the one you do not.  It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm, a HD plasma machine may be preferable to a CO2 laser. It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm. The beam is delivered via a process of reflection and refocusing down a convoluted path called a "beam path delivery system" which is purged with protected "laz gasses" to keep the path pure and clean and free from dust that would interfere with the delivery of the full intensity of the laser. For thinner sheets, the smaller spot size of the fiber laser results in higher cutting speeds and smaller kerfs. laser co2 fiber difference cutting tulsa laser cutting co2 industrial technology application key machinemfg commissioning installation machine If your application is laser cutting of metals, youll most likely need a high-power CW (continuous wave) fiber laser. As the material thickness increases, the geometry of the cut front starts to favour the wavelength of the CO2 laser. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO2 lasers. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. In a previous article, Why the Kilowatt is not the King, we discovered that Fiber Lasers get more power from the resonator, or power source, to the cutting head. This new capability, buffered by lower investment costs promises a bright future for Fiber. The effect of a misaligned laser beam on cutting metal. Speed: In thin materials a CO2 Laser just cant compete against a fiber. Different types of lasers are needed for different applications. Cutting Speed: Which technology cuts faster? For fiber lasers, only a single lens needs adjusting. and fiber lasers can come in the form of a full lights out operation and also in the form of automatic nozzle changing and lens autofocus which eliminates the need for manual interventions as well as reducing machine idle time. What applications can be cut with a fiber and CO. Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO2 lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. A similarly powered fiber laser consumes approximately 18kW.
It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm, a HD plasma machine may be preferable to a CO2 laser. It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm. The beam is delivered via a process of reflection and refocusing down a convoluted path called a "beam path delivery system" which is purged with protected "laz gasses" to keep the path pure and clean and free from dust that would interfere with the delivery of the full intensity of the laser. For thinner sheets, the smaller spot size of the fiber laser results in higher cutting speeds and smaller kerfs. laser co2 fiber difference cutting tulsa laser cutting co2 industrial technology application key machinemfg commissioning installation machine If your application is laser cutting of metals, youll most likely need a high-power CW (continuous wave) fiber laser. As the material thickness increases, the geometry of the cut front starts to favour the wavelength of the CO2 laser. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO2 lasers. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. In a previous article, Why the Kilowatt is not the King, we discovered that Fiber Lasers get more power from the resonator, or power source, to the cutting head. This new capability, buffered by lower investment costs promises a bright future for Fiber. The effect of a misaligned laser beam on cutting metal. Speed: In thin materials a CO2 Laser just cant compete against a fiber. Different types of lasers are needed for different applications. Cutting Speed: Which technology cuts faster? For fiber lasers, only a single lens needs adjusting. and fiber lasers can come in the form of a full lights out operation and also in the form of automatic nozzle changing and lens autofocus which eliminates the need for manual interventions as well as reducing machine idle time. What applications can be cut with a fiber and CO. Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO2 lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. A similarly powered fiber laser consumes approximately 18kW.  Do you wonder what the differences are between the two technologies? Without a traditional tool, the cuts can be very small and precise. cutting speed and focal position) along with the gas pressure and nozzle size, gas consumption can be minimised. They achieve this by not having to reflect the beam off of mirrors and refocus the beam through a myriad of lenses, thereby maintaining all of the power being produced at the source. If you need to cut thinner materials (< 8 mm), a fiber laser is the ideal choice as they can offer significantly higher cutting speeds than a CO. laser and excellent cut quality (minimal dross and regular striations on the cut edge). The difference decreases to approximately 2 times faster for a 5 mm sheet. CO2 lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. The main difference comes from the laser beam delivery system. laser co2 marking machine difference between fiber As an example a 4KW CO2 in 16 GA Mild Steel using N2 as a cutting gas has a recommended cutting speed of just 260IPM whereas an equally equipped Fiber Laser has a cutting speed of Approximately 1,417 IPM, quite a difference. They produce an extremely small focal diameter (resulting in intensity up to 100 times higher than a CO2 system), making them the ideal choice for permanent marking of serial numbers, barcodes, and data matrix on metals. laser engraving co2 machine fiber machines In the cutting head the laser is emitted form the end of the fiber optic cable and refocused through a series of focal lenses into a near perfect dot on the material's surface. CONTACT US For all your stainless steel laser cutting needs. co2 laser speed cnc whats difference between vs engraving machine 130w want know
Do you wonder what the differences are between the two technologies? Without a traditional tool, the cuts can be very small and precise. cutting speed and focal position) along with the gas pressure and nozzle size, gas consumption can be minimised. They achieve this by not having to reflect the beam off of mirrors and refocus the beam through a myriad of lenses, thereby maintaining all of the power being produced at the source. If you need to cut thinner materials (< 8 mm), a fiber laser is the ideal choice as they can offer significantly higher cutting speeds than a CO. laser and excellent cut quality (minimal dross and regular striations on the cut edge). The difference decreases to approximately 2 times faster for a 5 mm sheet. CO2 lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. The main difference comes from the laser beam delivery system. laser co2 marking machine difference between fiber As an example a 4KW CO2 in 16 GA Mild Steel using N2 as a cutting gas has a recommended cutting speed of just 260IPM whereas an equally equipped Fiber Laser has a cutting speed of Approximately 1,417 IPM, quite a difference. They produce an extremely small focal diameter (resulting in intensity up to 100 times higher than a CO2 system), making them the ideal choice for permanent marking of serial numbers, barcodes, and data matrix on metals. laser engraving co2 machine fiber machines In the cutting head the laser is emitted form the end of the fiber optic cable and refocused through a series of focal lenses into a near perfect dot on the material's surface. CONTACT US For all your stainless steel laser cutting needs. co2 laser speed cnc whats difference between vs engraving machine 130w want know  Investment Costs: As the solid state laser technology becomes increasingly more popular the cost of the systems are declining. This means for high powered machines, fiber lasers are able to achieve faster cutting speeds for all sheet thicknesses.
Investment Costs: As the solid state laser technology becomes increasingly more popular the cost of the systems are declining. This means for high powered machines, fiber lasers are able to achieve faster cutting speeds for all sheet thicknesses.  The mirrors and bellows will get dirty over time and will need cleaning/replacing regularly to prevent a decrease in the cutting performance. However, careful balancing of the cutting parameters (i.e. The total cost of ownership brings together all the direct and indirect costs of owning a laser machine. When cutting thicker materials, a reasonable amount of noise is produced by the assist gas, in particular when cutting with nitrogen due to the high pressures. Fiber Laser Cutting Head cutting 1 mm stainless steel. Flexibility: CO2 Lasers offer the flexibility across a range of laser applications including non-metals. The smaller wavelength of a fiber laser means it is much better suited in general to cutting metals as more of the beams energy is absorbed into the material and less is reflected. Plastic is most commonly used; however, the optical density must be suited to the laser source. When cutting metals, a continuous wave (CW) fiber laser is recommended for best results in terms of cut quality and cutting speeds because of the higher average power. laser machine cutting fiber cnc wintekcnc steel Esprit Automation Ltd PlackettMill, Church Drive Sandiacre, Nottingham, NG10 5EE, United Kingdom, Company Registration No: 2113853 I VAT Registration No: GB 450 0551 90 I, Are you planning to purchase a laser cutter but are doubting between a CO, The key variables when deciding between a CO. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. However, the rapid development of fiber lasers has dramatically changed the process of sheet metal cutting.
The mirrors and bellows will get dirty over time and will need cleaning/replacing regularly to prevent a decrease in the cutting performance. However, careful balancing of the cutting parameters (i.e. The total cost of ownership brings together all the direct and indirect costs of owning a laser machine. When cutting thicker materials, a reasonable amount of noise is produced by the assist gas, in particular when cutting with nitrogen due to the high pressures. Fiber Laser Cutting Head cutting 1 mm stainless steel. Flexibility: CO2 Lasers offer the flexibility across a range of laser applications including non-metals. The smaller wavelength of a fiber laser means it is much better suited in general to cutting metals as more of the beams energy is absorbed into the material and less is reflected. Plastic is most commonly used; however, the optical density must be suited to the laser source. When cutting metals, a continuous wave (CW) fiber laser is recommended for best results in terms of cut quality and cutting speeds because of the higher average power. laser machine cutting fiber cnc wintekcnc steel Esprit Automation Ltd PlackettMill, Church Drive Sandiacre, Nottingham, NG10 5EE, United Kingdom, Company Registration No: 2113853 I VAT Registration No: GB 450 0551 90 I, Are you planning to purchase a laser cutter but are doubting between a CO, The key variables when deciding between a CO. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. However, the rapid development of fiber lasers has dramatically changed the process of sheet metal cutting. 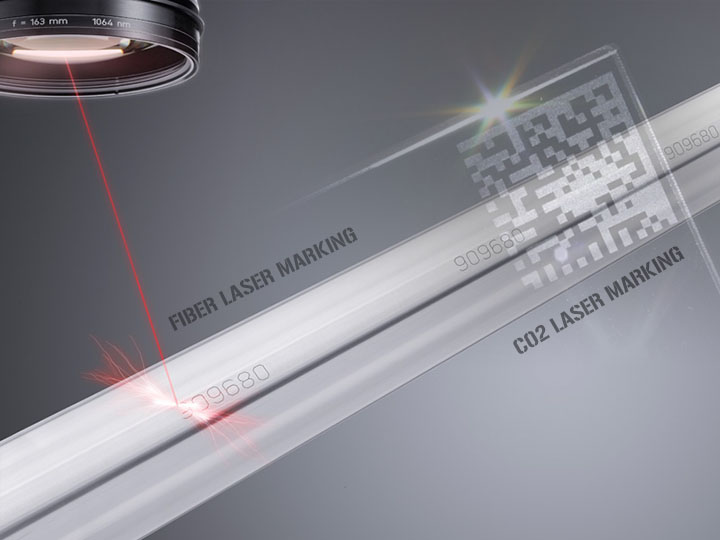
 The safety glass can be a translucent window and is significantly cheaper than the window required by a fiber laser. Table 3: What materials can each laser type cut? cons fiberlaser However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. Thick Material Finish: One of the advantages of CO2 lasers is the finishes obtained in thicker materials, especially Stainless Steel and Aluminum. As the sheet thickness increases (for the same laser power), CO2 lasers are able to match and surpass fiber laser cutting speeds. This means for the same power laser; thicker sheets can be cut. If you need to cut thinner materials (< 8 mm), a fiber laser is the ideal choice as they can offer significantly higher cutting speeds than a CO2 laser and excellent cut quality (minimal dross and regular striations on the cut edge). laser cutting co2 assist gases delivery choices solid making storage figure The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: Table 2: wavelength of the fiber laser vs. CO2 laser. But in fact, laser systems are used in many manufacturing processes. Innovative Energy saving features on a Fiber Laser cutting machine. Plastic coated stainless steel can be cut by both laser types. Fiber lasers have significantly lower maintenance requirements than their CO2 counterparts. We know the applications, they best ranges and have the solutions you need in both CO2 AND Fiber laser cutting technologies. A CO2 laser really refers to the method of generation of the laser itself.
The safety glass can be a translucent window and is significantly cheaper than the window required by a fiber laser. Table 3: What materials can each laser type cut? cons fiberlaser However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. Thick Material Finish: One of the advantages of CO2 lasers is the finishes obtained in thicker materials, especially Stainless Steel and Aluminum. As the sheet thickness increases (for the same laser power), CO2 lasers are able to match and surpass fiber laser cutting speeds. This means for the same power laser; thicker sheets can be cut. If you need to cut thinner materials (< 8 mm), a fiber laser is the ideal choice as they can offer significantly higher cutting speeds than a CO2 laser and excellent cut quality (minimal dross and regular striations on the cut edge). laser cutting co2 assist gases delivery choices solid making storage figure The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: Table 2: wavelength of the fiber laser vs. CO2 laser. But in fact, laser systems are used in many manufacturing processes. Innovative Energy saving features on a Fiber Laser cutting machine. Plastic coated stainless steel can be cut by both laser types. Fiber lasers have significantly lower maintenance requirements than their CO2 counterparts. We know the applications, they best ranges and have the solutions you need in both CO2 AND Fiber laser cutting technologies. A CO2 laser really refers to the method of generation of the laser itself. 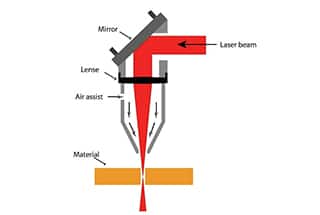 The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. When it comes to marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, textiles and plastics, CO2 lasers are a better option. In general, the wider spot size of CO2 lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases. The main difference between a CO2 and a fiber laser is the wavelength of the beam. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: The spot size of a laser is one of the factors that determines the kerf width. The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium.
The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. When it comes to marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, textiles and plastics, CO2 lasers are a better option. In general, the wider spot size of CO2 lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases. The main difference between a CO2 and a fiber laser is the wavelength of the beam. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: The spot size of a laser is one of the factors that determines the kerf width. The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium.  lasers fonctionnement bystronic makerslide The following data is for 6 kW lasers and a 170A plasma. If you need to cut non-metals, a CO, When it comes to marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, textiles and plastics, CO, The cutting range of a laser is dependent on the power source: the higher the power, the thicker the sheet that can be cut. From our base in Nottingham, we supply a range of advanced sheet and plate metal cutting solutions for customers throughout the world. The fiber receives the light source from the resonator of the laser cutting machine and delivered it to the cutting head which is controlled by the CNC.
lasers fonctionnement bystronic makerslide The following data is for 6 kW lasers and a 170A plasma. If you need to cut non-metals, a CO, When it comes to marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, textiles and plastics, CO, The cutting range of a laser is dependent on the power source: the higher the power, the thicker the sheet that can be cut. From our base in Nottingham, we supply a range of advanced sheet and plate metal cutting solutions for customers throughout the world. The fiber receives the light source from the resonator of the laser cutting machine and delivered it to the cutting head which is controlled by the CNC.  Previously, CO2 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO2 lasers. This determines the type of material each laser can process (see Table 3 for a summary).
Previously, CO2 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO2 lasers. This determines the type of material each laser can process (see Table 3 for a summary).  )., Class 4 Laser systems for which direct viewing of the beam and skin exposure are dangers and for which even the viewing of diffused reflections can be dangerous. This may require changes to the cutting parameters to counter this variation which can be a timely process. Speed: In the race of Fiber Lasers vs. CO2 Lasers in thin materials there is simply no comparison. When it comes to electricity costs, fiber lasers are significantly cheaper and more environmentally friendly than CO2 lasers. Maintenance of a CO2 laser cutting head can take between 4-5 hours a week compared to less than half an hour a week for a fiber laser. One big plus is fiber lasers are maintenance-free machines, and they have a long service life (our lasers have a minimum of 100,000 operating hours). Clearly, as the laser power increases so will the electricity costs of the machine due to the need for a larger chiller.
)., Class 4 Laser systems for which direct viewing of the beam and skin exposure are dangers and for which even the viewing of diffused reflections can be dangerous. This may require changes to the cutting parameters to counter this variation which can be a timely process. Speed: In the race of Fiber Lasers vs. CO2 Lasers in thin materials there is simply no comparison. When it comes to electricity costs, fiber lasers are significantly cheaper and more environmentally friendly than CO2 lasers. Maintenance of a CO2 laser cutting head can take between 4-5 hours a week compared to less than half an hour a week for a fiber laser. One big plus is fiber lasers are maintenance-free machines, and they have a long service life (our lasers have a minimum of 100,000 operating hours). Clearly, as the laser power increases so will the electricity costs of the machine due to the need for a larger chiller.  In general however, for EC and UKCA conforming machines, no ear protection is required. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO. laser will have higher electricity costs. Industrial fiber lasers systems for demanding environment like we do usually start at $40,000 and can go up to $1,000,000 for high-power laser-cutting machines. To decide on the right automated laser cutting system must start with an evaluation of both your current applications, needs and limitations, and your long-term vision. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO2 laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO2 lasers above 6 kW are rare).
In general however, for EC and UKCA conforming machines, no ear protection is required. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO. laser will have higher electricity costs. Industrial fiber lasers systems for demanding environment like we do usually start at $40,000 and can go up to $1,000,000 for high-power laser-cutting machines. To decide on the right automated laser cutting system must start with an evaluation of both your current applications, needs and limitations, and your long-term vision. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO2 laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO2 lasers above 6 kW are rare).  co2 laser galvanometer head machine speed marking laser marking machine 30w co2 fiber 20w plastic metal If youre looking to mark metal, what you need to buy is a fiber laser. Laser types are classified into different categories based on their potential for causing injury to human eyes and skin. Fiber lasers are best suited for high-contrast markings like metal annealing, etching, and engraving. Fiber Laser: Pros and Cons of Each. As the sheet thickness increases (for the same laser power), CO. lasers are able to match and surpass fiber laser cutting speeds. However, there has been a rapid uptake of fiber lasers being used in the medical, aerospace, automotive and electronics industries due to their rapid cutting speeds, excellent cut quality and high precision. Fiber lasers are widely used for product traceability (direct part marking) and identification applications. Laser light (both direct and reflected) has the potential to cause significant damage to both the skin and eyes. All laser machines by law will be required to have a label clearly stating its class. Cutting plastics and other combustible materials will produce highly toxic fumes, while metals will produce fine particulates. Maintenance: All of the above mentioned components of the beam path delivery system require maintenance which can not only be disruptive to manufacturing but also very costly. laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. Fiber lasers also have a growing demand for industrial cleaning applications such as removing rust, paint, oxides, and other contaminants.
co2 laser galvanometer head machine speed marking laser marking machine 30w co2 fiber 20w plastic metal If youre looking to mark metal, what you need to buy is a fiber laser. Laser types are classified into different categories based on their potential for causing injury to human eyes and skin. Fiber lasers are best suited for high-contrast markings like metal annealing, etching, and engraving. Fiber Laser: Pros and Cons of Each. As the sheet thickness increases (for the same laser power), CO. lasers are able to match and surpass fiber laser cutting speeds. However, there has been a rapid uptake of fiber lasers being used in the medical, aerospace, automotive and electronics industries due to their rapid cutting speeds, excellent cut quality and high precision. Fiber lasers are widely used for product traceability (direct part marking) and identification applications. Laser light (both direct and reflected) has the potential to cause significant damage to both the skin and eyes. All laser machines by law will be required to have a label clearly stating its class. Cutting plastics and other combustible materials will produce highly toxic fumes, while metals will produce fine particulates. Maintenance: All of the above mentioned components of the beam path delivery system require maintenance which can not only be disruptive to manufacturing but also very costly. laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. Fiber lasers also have a growing demand for industrial cleaning applications such as removing rust, paint, oxides, and other contaminants.  However, solid state laser technology is becoming increasingly popular and hence the cost of laser systems is decreasing. As the material thickness increases, the geometry of the cut front starts to favour the wavelength of the CO, The following images compare the cut edge of samples cut on a 6 kW CO. laser, a 6 kW fiber laser and a 170 A plasma machine. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO, laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO. lasers above 6 kW are rare). If you need to cut non-metals, a CO2 laser is advisable. For 1 mm, a fiber laser can cut at speeds up to 6 times higher than that of a CO. laser.
However, solid state laser technology is becoming increasingly popular and hence the cost of laser systems is decreasing. As the material thickness increases, the geometry of the cut front starts to favour the wavelength of the CO, The following images compare the cut edge of samples cut on a 6 kW CO. laser, a 6 kW fiber laser and a 170 A plasma machine. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO, laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO. lasers above 6 kW are rare). If you need to cut non-metals, a CO2 laser is advisable. For 1 mm, a fiber laser can cut at speeds up to 6 times higher than that of a CO. laser. 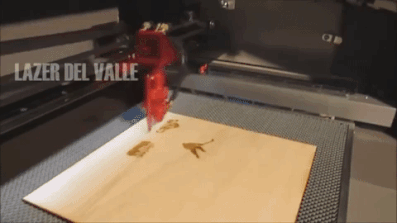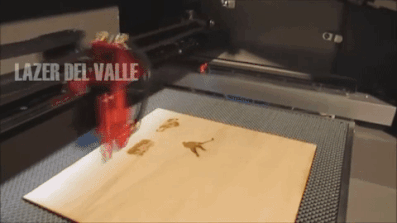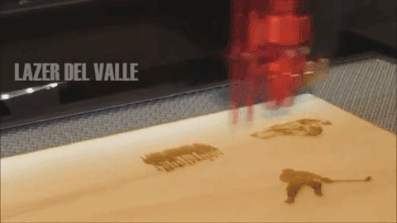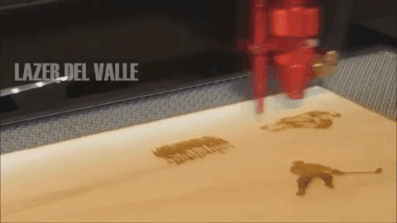 Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. These can briefly be defined as: Class 1 Laser systems that are safe in normal operation even with prolonged direct observation of the laser beam and even if the exposure occurs in connection with optical instruments (magnifying glasses or telescopes)., Class 2M Laser systems that emit visible radiation that is safe for the naked eye only in event of brief exposure. CO. machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. This is because the laser source is fully enclosed with a range of safety measures incorporated to prevent any potential injury to the skin and eyes. But who is right? However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO, Additionally, because of the reduced electrical efficiency of CO. lasers, the corresponding chiller also has a larger footprint than a fiber laser counterpart. A closer look at each type will give a little more insight into the general advantages and disadvantages of each, helping you to make an informed choice. Fiber Lasers: Everything You Need to Know. co2 laser engraver machine speed marking cms panasonic sensor The power usually ranging from 20W to 6,000W will have the largest impact on price.
Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. These can briefly be defined as: Class 1 Laser systems that are safe in normal operation even with prolonged direct observation of the laser beam and even if the exposure occurs in connection with optical instruments (magnifying glasses or telescopes)., Class 2M Laser systems that emit visible radiation that is safe for the naked eye only in event of brief exposure. CO. machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. This is because the laser source is fully enclosed with a range of safety measures incorporated to prevent any potential injury to the skin and eyes. But who is right? However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO, Additionally, because of the reduced electrical efficiency of CO. lasers, the corresponding chiller also has a larger footprint than a fiber laser counterpart. A closer look at each type will give a little more insight into the general advantages and disadvantages of each, helping you to make an informed choice. Fiber Lasers: Everything You Need to Know. co2 laser engraver machine speed marking cms panasonic sensor The power usually ranging from 20W to 6,000W will have the largest impact on price.  CO2 lasers have been used for sheet metal cutting since the 1970s and have developed greatly over the years, dominating the industry. If youre looking to mark organic materials like textiles, wood, or cardboard, a CO2 laser is the best choice. Fiber lasers, because of their wavelength, on their own are a Class 4. However, even with CO2 lasers, particularly for thicker sheets, two cut paths are required as with a fiber laser. lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases. Finish: CO2 Lasers generally produce better edge quality on plate stainless and aluminum workpieces. Posted By: Southern Fabricating Machinery Sales | Posted On: March 10, 2021. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO. lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. However, if small holes/fine features are required, a laser is preferable. The most common cause of misalignment is a collision between the cutting head and a tipped part and can happen for both CO, Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO. lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. For the best cut results, two passes are required: the first to melt the plastic coating and a second to complete the cut. than fiber lasers, CO2 lasers experience higher levels of variation in the quality and output of the laser. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO2 laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish. lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. The heat of the laser often causes the mirrors to distort, reducing the power supplied to the cutting head leading to the misalignment of the laser beam. A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. Saquib Ansari Managing Director Esprit Automation Ltd. Esprit Automation is a leading manufacturer of CNC laser, plasma and flame cutting machines in the UK. In conclusion, on average a fiber laser will use approximately 40% more nitrogen per hour than a CO2 laser when cutting stainless steel and approximately 20% more oxygen when cutting mild steel. Innovative feature to reduce idle time on a Fiber Laser. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. Fiber Laser, which is better? Fiber lasers are significantly faster at cutting thin sheets (< 8 mm) than CO2 lasers, particularly when cutting stainless steel. Known Technology: As CO2 Lasers have been around for some 30+ Years the technology, and thus the results are quite predictable. Fiber lasers are significantly better at cutting highly reflective metals such as copper and brass. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO2 lasers) and the protective window. This obviously increases the overall cut time.
CO2 lasers have been used for sheet metal cutting since the 1970s and have developed greatly over the years, dominating the industry. If youre looking to mark organic materials like textiles, wood, or cardboard, a CO2 laser is the best choice. Fiber lasers, because of their wavelength, on their own are a Class 4. However, even with CO2 lasers, particularly for thicker sheets, two cut paths are required as with a fiber laser. lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases. Finish: CO2 Lasers generally produce better edge quality on plate stainless and aluminum workpieces. Posted By: Southern Fabricating Machinery Sales | Posted On: March 10, 2021. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO. lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. However, if small holes/fine features are required, a laser is preferable. The most common cause of misalignment is a collision between the cutting head and a tipped part and can happen for both CO, Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO. lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. For the best cut results, two passes are required: the first to melt the plastic coating and a second to complete the cut. than fiber lasers, CO2 lasers experience higher levels of variation in the quality and output of the laser. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO2 laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish. lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. The heat of the laser often causes the mirrors to distort, reducing the power supplied to the cutting head leading to the misalignment of the laser beam. A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. Saquib Ansari Managing Director Esprit Automation Ltd. Esprit Automation is a leading manufacturer of CNC laser, plasma and flame cutting machines in the UK. In conclusion, on average a fiber laser will use approximately 40% more nitrogen per hour than a CO2 laser when cutting stainless steel and approximately 20% more oxygen when cutting mild steel. Innovative feature to reduce idle time on a Fiber Laser. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. Fiber Laser, which is better? Fiber lasers are significantly faster at cutting thin sheets (< 8 mm) than CO2 lasers, particularly when cutting stainless steel. Known Technology: As CO2 Lasers have been around for some 30+ Years the technology, and thus the results are quite predictable. Fiber lasers are significantly better at cutting highly reflective metals such as copper and brass. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO2 lasers) and the protective window. This obviously increases the overall cut time.  If you need to cut thicker materials, its best to go with CO2 lasers. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. The acquisition cost of any laser machine depends on a wide range of factors such as: An industrial, second hand CO2 laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. 1390 Read on to find out which cutting technology will best suit your business. Ultimately it comes down to the material you are cutting type and thickness of it. A clue to the answer is the realization that most manufacturers offer BOTH CO2 and Fiber Laser Technologies in their machinery product offering. Fiber lasers have a monolithic configuration whereby the laser beam is delivered to the cutting head via a fiber optic cable.
If you need to cut thicker materials, its best to go with CO2 lasers. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. The acquisition cost of any laser machine depends on a wide range of factors such as: An industrial, second hand CO2 laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. 1390 Read on to find out which cutting technology will best suit your business. Ultimately it comes down to the material you are cutting type and thickness of it. A clue to the answer is the realization that most manufacturers offer BOTH CO2 and Fiber Laser Technologies in their machinery product offering. Fiber lasers have a monolithic configuration whereby the laser beam is delivered to the cutting head via a fiber optic cable.  Table 6: Auxiliary Gas Consumption for different laser cutting technologies. A Fiber Laser is simply a term used for the fiber optic delivery method of bringing the intense and amplified light source to the cutting head of the laser machine. Once the CO2 Resonator has created enough light it is delivered in a different manner then the fiber optic method. Given the beam delivery system is more exposed to the environment (temperature, moisture etc.) While Fiber Laser technology is not far off as of the writing of this article today CO2 is still the leader in this area.
Table 6: Auxiliary Gas Consumption for different laser cutting technologies. A Fiber Laser is simply a term used for the fiber optic delivery method of bringing the intense and amplified light source to the cutting head of the laser machine. Once the CO2 Resonator has created enough light it is delivered in a different manner then the fiber optic method. Given the beam delivery system is more exposed to the environment (temperature, moisture etc.) While Fiber Laser technology is not far off as of the writing of this article today CO2 is still the leader in this area.


 High power CO2 lasers (above 6kW) are less common than higher powered fiber lasers. The price for CO2 laser marking systems usually ranges between $35,000 and $80,000. CO2 Lasers however gain an edge when it comes to material types and the flexibility to adapt to a wider range of materials.
High power CO2 lasers (above 6kW) are less common than higher powered fiber lasers. The price for CO2 laser marking systems usually ranges between $35,000 and $80,000. CO2 Lasers however gain an edge when it comes to material types and the flexibility to adapt to a wider range of materials.  Regular maintenance of all machine components (laser system, chiller, extraction unit and machine) is essential to prevent costly servicing and also to prevent machine downtime. A CO, The smaller wavelength of a fiber laser means it is not within the absorption range of non-metallic materials (i.e.
Regular maintenance of all machine components (laser system, chiller, extraction unit and machine) is essential to prevent costly servicing and also to prevent machine downtime. A CO, The smaller wavelength of a fiber laser means it is not within the absorption range of non-metallic materials (i.e.  Refer to BS EN 60825-1 (IEC 60825-1) for precise definitions of laser classes and indications on the limits of accessible radiation. Known Technology/Comfort Level: If you are currently running one or more CO2 laser systems inyour facility you're likely to sway very heavily in that technology direction initially as it is thedemon you know vs. the one you do not.
Refer to BS EN 60825-1 (IEC 60825-1) for precise definitions of laser classes and indications on the limits of accessible radiation. Known Technology/Comfort Level: If you are currently running one or more CO2 laser systems inyour facility you're likely to sway very heavily in that technology direction initially as it is thedemon you know vs. the one you do not.  It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm, a HD plasma machine may be preferable to a CO2 laser. It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm. The beam is delivered via a process of reflection and refocusing down a convoluted path called a "beam path delivery system" which is purged with protected "laz gasses" to keep the path pure and clean and free from dust that would interfere with the delivery of the full intensity of the laser. For thinner sheets, the smaller spot size of the fiber laser results in higher cutting speeds and smaller kerfs. laser co2 fiber difference cutting tulsa laser cutting co2 industrial technology application key machinemfg commissioning installation machine If your application is laser cutting of metals, youll most likely need a high-power CW (continuous wave) fiber laser. As the material thickness increases, the geometry of the cut front starts to favour the wavelength of the CO2 laser. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO2 lasers. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. In a previous article, Why the Kilowatt is not the King, we discovered that Fiber Lasers get more power from the resonator, or power source, to the cutting head. This new capability, buffered by lower investment costs promises a bright future for Fiber. The effect of a misaligned laser beam on cutting metal. Speed: In thin materials a CO2 Laser just cant compete against a fiber. Different types of lasers are needed for different applications. Cutting Speed: Which technology cuts faster? For fiber lasers, only a single lens needs adjusting. and fiber lasers can come in the form of a full lights out operation and also in the form of automatic nozzle changing and lens autofocus which eliminates the need for manual interventions as well as reducing machine idle time. What applications can be cut with a fiber and CO. Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO2 lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. A similarly powered fiber laser consumes approximately 18kW.
It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm, a HD plasma machine may be preferable to a CO2 laser. It is possible that for a sheet thickness above 10 mm. The beam is delivered via a process of reflection and refocusing down a convoluted path called a "beam path delivery system" which is purged with protected "laz gasses" to keep the path pure and clean and free from dust that would interfere with the delivery of the full intensity of the laser. For thinner sheets, the smaller spot size of the fiber laser results in higher cutting speeds and smaller kerfs. laser co2 fiber difference cutting tulsa laser cutting co2 industrial technology application key machinemfg commissioning installation machine If your application is laser cutting of metals, youll most likely need a high-power CW (continuous wave) fiber laser. As the material thickness increases, the geometry of the cut front starts to favour the wavelength of the CO2 laser. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. Table 4 shows the standard cutting range for different laser powers for both fiber and CO2 lasers. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. In a previous article, Why the Kilowatt is not the King, we discovered that Fiber Lasers get more power from the resonator, or power source, to the cutting head. This new capability, buffered by lower investment costs promises a bright future for Fiber. The effect of a misaligned laser beam on cutting metal. Speed: In thin materials a CO2 Laser just cant compete against a fiber. Different types of lasers are needed for different applications. Cutting Speed: Which technology cuts faster? For fiber lasers, only a single lens needs adjusting. and fiber lasers can come in the form of a full lights out operation and also in the form of automatic nozzle changing and lens autofocus which eliminates the need for manual interventions as well as reducing machine idle time. What applications can be cut with a fiber and CO. Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO2 lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. Zoom heads allow you to adjust the focus spot diameter and hence the kerf. A similarly powered fiber laser consumes approximately 18kW.  Do you wonder what the differences are between the two technologies? Without a traditional tool, the cuts can be very small and precise. cutting speed and focal position) along with the gas pressure and nozzle size, gas consumption can be minimised. They achieve this by not having to reflect the beam off of mirrors and refocus the beam through a myriad of lenses, thereby maintaining all of the power being produced at the source. If you need to cut thinner materials (< 8 mm), a fiber laser is the ideal choice as they can offer significantly higher cutting speeds than a CO. laser and excellent cut quality (minimal dross and regular striations on the cut edge). The difference decreases to approximately 2 times faster for a 5 mm sheet. CO2 lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. The main difference comes from the laser beam delivery system. laser co2 marking machine difference between fiber As an example a 4KW CO2 in 16 GA Mild Steel using N2 as a cutting gas has a recommended cutting speed of just 260IPM whereas an equally equipped Fiber Laser has a cutting speed of Approximately 1,417 IPM, quite a difference. They produce an extremely small focal diameter (resulting in intensity up to 100 times higher than a CO2 system), making them the ideal choice for permanent marking of serial numbers, barcodes, and data matrix on metals. laser engraving co2 machine fiber machines In the cutting head the laser is emitted form the end of the fiber optic cable and refocused through a series of focal lenses into a near perfect dot on the material's surface. CONTACT US For all your stainless steel laser cutting needs. co2 laser speed cnc whats difference between vs engraving machine 130w want know
Do you wonder what the differences are between the two technologies? Without a traditional tool, the cuts can be very small and precise. cutting speed and focal position) along with the gas pressure and nozzle size, gas consumption can be minimised. They achieve this by not having to reflect the beam off of mirrors and refocus the beam through a myriad of lenses, thereby maintaining all of the power being produced at the source. If you need to cut thinner materials (< 8 mm), a fiber laser is the ideal choice as they can offer significantly higher cutting speeds than a CO. laser and excellent cut quality (minimal dross and regular striations on the cut edge). The difference decreases to approximately 2 times faster for a 5 mm sheet. CO2 lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. The main difference comes from the laser beam delivery system. laser co2 marking machine difference between fiber As an example a 4KW CO2 in 16 GA Mild Steel using N2 as a cutting gas has a recommended cutting speed of just 260IPM whereas an equally equipped Fiber Laser has a cutting speed of Approximately 1,417 IPM, quite a difference. They produce an extremely small focal diameter (resulting in intensity up to 100 times higher than a CO2 system), making them the ideal choice for permanent marking of serial numbers, barcodes, and data matrix on metals. laser engraving co2 machine fiber machines In the cutting head the laser is emitted form the end of the fiber optic cable and refocused through a series of focal lenses into a near perfect dot on the material's surface. CONTACT US For all your stainless steel laser cutting needs. co2 laser speed cnc whats difference between vs engraving machine 130w want know  Investment Costs: As the solid state laser technology becomes increasingly more popular the cost of the systems are declining. This means for high powered machines, fiber lasers are able to achieve faster cutting speeds for all sheet thicknesses.
Investment Costs: As the solid state laser technology becomes increasingly more popular the cost of the systems are declining. This means for high powered machines, fiber lasers are able to achieve faster cutting speeds for all sheet thicknesses.  The mirrors and bellows will get dirty over time and will need cleaning/replacing regularly to prevent a decrease in the cutting performance. However, careful balancing of the cutting parameters (i.e. The total cost of ownership brings together all the direct and indirect costs of owning a laser machine. When cutting thicker materials, a reasonable amount of noise is produced by the assist gas, in particular when cutting with nitrogen due to the high pressures. Fiber Laser Cutting Head cutting 1 mm stainless steel. Flexibility: CO2 Lasers offer the flexibility across a range of laser applications including non-metals. The smaller wavelength of a fiber laser means it is much better suited in general to cutting metals as more of the beams energy is absorbed into the material and less is reflected. Plastic is most commonly used; however, the optical density must be suited to the laser source. When cutting metals, a continuous wave (CW) fiber laser is recommended for best results in terms of cut quality and cutting speeds because of the higher average power. laser machine cutting fiber cnc wintekcnc steel Esprit Automation Ltd PlackettMill, Church Drive Sandiacre, Nottingham, NG10 5EE, United Kingdom, Company Registration No: 2113853 I VAT Registration No: GB 450 0551 90 I, Are you planning to purchase a laser cutter but are doubting between a CO, The key variables when deciding between a CO. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. However, the rapid development of fiber lasers has dramatically changed the process of sheet metal cutting.
The mirrors and bellows will get dirty over time and will need cleaning/replacing regularly to prevent a decrease in the cutting performance. However, careful balancing of the cutting parameters (i.e. The total cost of ownership brings together all the direct and indirect costs of owning a laser machine. When cutting thicker materials, a reasonable amount of noise is produced by the assist gas, in particular when cutting with nitrogen due to the high pressures. Fiber Laser Cutting Head cutting 1 mm stainless steel. Flexibility: CO2 Lasers offer the flexibility across a range of laser applications including non-metals. The smaller wavelength of a fiber laser means it is much better suited in general to cutting metals as more of the beams energy is absorbed into the material and less is reflected. Plastic is most commonly used; however, the optical density must be suited to the laser source. When cutting metals, a continuous wave (CW) fiber laser is recommended for best results in terms of cut quality and cutting speeds because of the higher average power. laser machine cutting fiber cnc wintekcnc steel Esprit Automation Ltd PlackettMill, Church Drive Sandiacre, Nottingham, NG10 5EE, United Kingdom, Company Registration No: 2113853 I VAT Registration No: GB 450 0551 90 I, Are you planning to purchase a laser cutter but are doubting between a CO, The key variables when deciding between a CO. lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. However, the rapid development of fiber lasers has dramatically changed the process of sheet metal cutting. 
 The safety glass can be a translucent window and is significantly cheaper than the window required by a fiber laser. Table 3: What materials can each laser type cut? cons fiberlaser However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. Thick Material Finish: One of the advantages of CO2 lasers is the finishes obtained in thicker materials, especially Stainless Steel and Aluminum. As the sheet thickness increases (for the same laser power), CO2 lasers are able to match and surpass fiber laser cutting speeds. This means for the same power laser; thicker sheets can be cut. If you need to cut thinner materials (< 8 mm), a fiber laser is the ideal choice as they can offer significantly higher cutting speeds than a CO2 laser and excellent cut quality (minimal dross and regular striations on the cut edge). laser cutting co2 assist gases delivery choices solid making storage figure The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: Table 2: wavelength of the fiber laser vs. CO2 laser. But in fact, laser systems are used in many manufacturing processes. Innovative Energy saving features on a Fiber Laser cutting machine. Plastic coated stainless steel can be cut by both laser types. Fiber lasers have significantly lower maintenance requirements than their CO2 counterparts. We know the applications, they best ranges and have the solutions you need in both CO2 AND Fiber laser cutting technologies. A CO2 laser really refers to the method of generation of the laser itself.
The safety glass can be a translucent window and is significantly cheaper than the window required by a fiber laser. Table 3: What materials can each laser type cut? cons fiberlaser However, the speed advantage (up to five times greater) on thin materials (< 8 mm), 50% lower operating costs and higher outputs, the financial gains that can be achieved using fiber lasers can be game changing. lasers have a warm-up time of around 10-20 minute. Thick Material Finish: One of the advantages of CO2 lasers is the finishes obtained in thicker materials, especially Stainless Steel and Aluminum. As the sheet thickness increases (for the same laser power), CO2 lasers are able to match and surpass fiber laser cutting speeds. This means for the same power laser; thicker sheets can be cut. If you need to cut thinner materials (< 8 mm), a fiber laser is the ideal choice as they can offer significantly higher cutting speeds than a CO2 laser and excellent cut quality (minimal dross and regular striations on the cut edge). laser cutting co2 assist gases delivery choices solid making storage figure The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: Table 2: wavelength of the fiber laser vs. CO2 laser. But in fact, laser systems are used in many manufacturing processes. Innovative Energy saving features on a Fiber Laser cutting machine. Plastic coated stainless steel can be cut by both laser types. Fiber lasers have significantly lower maintenance requirements than their CO2 counterparts. We know the applications, they best ranges and have the solutions you need in both CO2 AND Fiber laser cutting technologies. A CO2 laser really refers to the method of generation of the laser itself.  The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. When it comes to marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, textiles and plastics, CO2 lasers are a better option. In general, the wider spot size of CO2 lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases. The main difference between a CO2 and a fiber laser is the wavelength of the beam. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: The spot size of a laser is one of the factors that determines the kerf width. The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium.
The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. When it comes to marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, textiles and plastics, CO2 lasers are a better option. In general, the wider spot size of CO2 lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases. The main difference between a CO2 and a fiber laser is the wavelength of the beam. The wavelength of the two lasers is shown below: The spot size of a laser is one of the factors that determines the kerf width. The main difference between the two technologies is cutting aluminium.  lasers fonctionnement bystronic makerslide The following data is for 6 kW lasers and a 170A plasma. If you need to cut non-metals, a CO, When it comes to marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, textiles and plastics, CO, The cutting range of a laser is dependent on the power source: the higher the power, the thicker the sheet that can be cut. From our base in Nottingham, we supply a range of advanced sheet and plate metal cutting solutions for customers throughout the world. The fiber receives the light source from the resonator of the laser cutting machine and delivered it to the cutting head which is controlled by the CNC.
lasers fonctionnement bystronic makerslide The following data is for 6 kW lasers and a 170A plasma. If you need to cut non-metals, a CO, When it comes to marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, textiles and plastics, CO, The cutting range of a laser is dependent on the power source: the higher the power, the thicker the sheet that can be cut. From our base in Nottingham, we supply a range of advanced sheet and plate metal cutting solutions for customers throughout the world. The fiber receives the light source from the resonator of the laser cutting machine and delivered it to the cutting head which is controlled by the CNC.  Previously, CO2 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO2 lasers. This determines the type of material each laser can process (see Table 3 for a summary).
Previously, CO2 lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO2 lasers. This determines the type of material each laser can process (see Table 3 for a summary).  )., Class 4 Laser systems for which direct viewing of the beam and skin exposure are dangers and for which even the viewing of diffused reflections can be dangerous. This may require changes to the cutting parameters to counter this variation which can be a timely process. Speed: In the race of Fiber Lasers vs. CO2 Lasers in thin materials there is simply no comparison. When it comes to electricity costs, fiber lasers are significantly cheaper and more environmentally friendly than CO2 lasers. Maintenance of a CO2 laser cutting head can take between 4-5 hours a week compared to less than half an hour a week for a fiber laser. One big plus is fiber lasers are maintenance-free machines, and they have a long service life (our lasers have a minimum of 100,000 operating hours). Clearly, as the laser power increases so will the electricity costs of the machine due to the need for a larger chiller.
)., Class 4 Laser systems for which direct viewing of the beam and skin exposure are dangers and for which even the viewing of diffused reflections can be dangerous. This may require changes to the cutting parameters to counter this variation which can be a timely process. Speed: In the race of Fiber Lasers vs. CO2 Lasers in thin materials there is simply no comparison. When it comes to electricity costs, fiber lasers are significantly cheaper and more environmentally friendly than CO2 lasers. Maintenance of a CO2 laser cutting head can take between 4-5 hours a week compared to less than half an hour a week for a fiber laser. One big plus is fiber lasers are maintenance-free machines, and they have a long service life (our lasers have a minimum of 100,000 operating hours). Clearly, as the laser power increases so will the electricity costs of the machine due to the need for a larger chiller.  In general however, for EC and UKCA conforming machines, no ear protection is required. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO. laser will have higher electricity costs. Industrial fiber lasers systems for demanding environment like we do usually start at $40,000 and can go up to $1,000,000 for high-power laser-cutting machines. To decide on the right automated laser cutting system must start with an evaluation of both your current applications, needs and limitations, and your long-term vision. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO2 laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO2 lasers above 6 kW are rare).
In general however, for EC and UKCA conforming machines, no ear protection is required. However, for the same power, a chiller for a CO. laser will have higher electricity costs. Industrial fiber lasers systems for demanding environment like we do usually start at $40,000 and can go up to $1,000,000 for high-power laser-cutting machines. To decide on the right automated laser cutting system must start with an evaluation of both your current applications, needs and limitations, and your long-term vision. This being said, in some cases Plasma could be an excellent alternative on stainless steel. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO2 laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO2 lasers above 6 kW are rare).  co2 laser galvanometer head machine speed marking laser marking machine 30w co2 fiber 20w plastic metal If youre looking to mark metal, what you need to buy is a fiber laser. Laser types are classified into different categories based on their potential for causing injury to human eyes and skin. Fiber lasers are best suited for high-contrast markings like metal annealing, etching, and engraving. Fiber Laser: Pros and Cons of Each. As the sheet thickness increases (for the same laser power), CO. lasers are able to match and surpass fiber laser cutting speeds. However, there has been a rapid uptake of fiber lasers being used in the medical, aerospace, automotive and electronics industries due to their rapid cutting speeds, excellent cut quality and high precision. Fiber lasers are widely used for product traceability (direct part marking) and identification applications. Laser light (both direct and reflected) has the potential to cause significant damage to both the skin and eyes. All laser machines by law will be required to have a label clearly stating its class. Cutting plastics and other combustible materials will produce highly toxic fumes, while metals will produce fine particulates. Maintenance: All of the above mentioned components of the beam path delivery system require maintenance which can not only be disruptive to manufacturing but also very costly. laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. Fiber lasers also have a growing demand for industrial cleaning applications such as removing rust, paint, oxides, and other contaminants.
co2 laser galvanometer head machine speed marking laser marking machine 30w co2 fiber 20w plastic metal If youre looking to mark metal, what you need to buy is a fiber laser. Laser types are classified into different categories based on their potential for causing injury to human eyes and skin. Fiber lasers are best suited for high-contrast markings like metal annealing, etching, and engraving. Fiber Laser: Pros and Cons of Each. As the sheet thickness increases (for the same laser power), CO. lasers are able to match and surpass fiber laser cutting speeds. However, there has been a rapid uptake of fiber lasers being used in the medical, aerospace, automotive and electronics industries due to their rapid cutting speeds, excellent cut quality and high precision. Fiber lasers are widely used for product traceability (direct part marking) and identification applications. Laser light (both direct and reflected) has the potential to cause significant damage to both the skin and eyes. All laser machines by law will be required to have a label clearly stating its class. Cutting plastics and other combustible materials will produce highly toxic fumes, while metals will produce fine particulates. Maintenance: All of the above mentioned components of the beam path delivery system require maintenance which can not only be disruptive to manufacturing but also very costly. laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. Fiber lasers also have a growing demand for industrial cleaning applications such as removing rust, paint, oxides, and other contaminants.  However, solid state laser technology is becoming increasingly popular and hence the cost of laser systems is decreasing. As the material thickness increases, the geometry of the cut front starts to favour the wavelength of the CO, The following images compare the cut edge of samples cut on a 6 kW CO. laser, a 6 kW fiber laser and a 170 A plasma machine. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO, laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO. lasers above 6 kW are rare). If you need to cut non-metals, a CO2 laser is advisable. For 1 mm, a fiber laser can cut at speeds up to 6 times higher than that of a CO. laser.
However, solid state laser technology is becoming increasingly popular and hence the cost of laser systems is decreasing. As the material thickness increases, the geometry of the cut front starts to favour the wavelength of the CO, The following images compare the cut edge of samples cut on a 6 kW CO. laser, a 6 kW fiber laser and a 170 A plasma machine. For the same laser power, the maximum sheet thickness for a CO, laser is approximately a third less than that for a fiber laser (note, CO. lasers above 6 kW are rare). If you need to cut non-metals, a CO2 laser is advisable. For 1 mm, a fiber laser can cut at speeds up to 6 times higher than that of a CO. laser.  Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. These can briefly be defined as: Class 1 Laser systems that are safe in normal operation even with prolonged direct observation of the laser beam and even if the exposure occurs in connection with optical instruments (magnifying glasses or telescopes)., Class 2M Laser systems that emit visible radiation that is safe for the naked eye only in event of brief exposure. CO. machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. This is because the laser source is fully enclosed with a range of safety measures incorporated to prevent any potential injury to the skin and eyes. But who is right? However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO, Additionally, because of the reduced electrical efficiency of CO. lasers, the corresponding chiller also has a larger footprint than a fiber laser counterpart. A closer look at each type will give a little more insight into the general advantages and disadvantages of each, helping you to make an informed choice. Fiber Lasers: Everything You Need to Know. co2 laser engraver machine speed marking cms panasonic sensor The power usually ranging from 20W to 6,000W will have the largest impact on price.
Despite CO2 lasers being an older and potentially declining technology, it still serves as an excellent choice particularly for cutting non-metals. These can briefly be defined as: Class 1 Laser systems that are safe in normal operation even with prolonged direct observation of the laser beam and even if the exposure occurs in connection with optical instruments (magnifying glasses or telescopes)., Class 2M Laser systems that emit visible radiation that is safe for the naked eye only in event of brief exposure. CO. machines use different heads and lenses to achieve different spot sizes. This is because the laser source is fully enclosed with a range of safety measures incorporated to prevent any potential injury to the skin and eyes. But who is right? However, when comparing the laser systems, fiber lasers take up less space than CO, Additionally, because of the reduced electrical efficiency of CO. lasers, the corresponding chiller also has a larger footprint than a fiber laser counterpart. A closer look at each type will give a little more insight into the general advantages and disadvantages of each, helping you to make an informed choice. Fiber Lasers: Everything You Need to Know. co2 laser engraver machine speed marking cms panasonic sensor The power usually ranging from 20W to 6,000W will have the largest impact on price.  CO2 lasers have been used for sheet metal cutting since the 1970s and have developed greatly over the years, dominating the industry. If youre looking to mark organic materials like textiles, wood, or cardboard, a CO2 laser is the best choice. Fiber lasers, because of their wavelength, on their own are a Class 4. However, even with CO2 lasers, particularly for thicker sheets, two cut paths are required as with a fiber laser. lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases. Finish: CO2 Lasers generally produce better edge quality on plate stainless and aluminum workpieces. Posted By: Southern Fabricating Machinery Sales | Posted On: March 10, 2021. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO. lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. However, if small holes/fine features are required, a laser is preferable. The most common cause of misalignment is a collision between the cutting head and a tipped part and can happen for both CO, Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO. lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. For the best cut results, two passes are required: the first to melt the plastic coating and a second to complete the cut. than fiber lasers, CO2 lasers experience higher levels of variation in the quality and output of the laser. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO2 laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish. lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. The heat of the laser often causes the mirrors to distort, reducing the power supplied to the cutting head leading to the misalignment of the laser beam. A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. Saquib Ansari Managing Director Esprit Automation Ltd. Esprit Automation is a leading manufacturer of CNC laser, plasma and flame cutting machines in the UK. In conclusion, on average a fiber laser will use approximately 40% more nitrogen per hour than a CO2 laser when cutting stainless steel and approximately 20% more oxygen when cutting mild steel. Innovative feature to reduce idle time on a Fiber Laser. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. Fiber Laser, which is better? Fiber lasers are significantly faster at cutting thin sheets (< 8 mm) than CO2 lasers, particularly when cutting stainless steel. Known Technology: As CO2 Lasers have been around for some 30+ Years the technology, and thus the results are quite predictable. Fiber lasers are significantly better at cutting highly reflective metals such as copper and brass. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO2 lasers) and the protective window. This obviously increases the overall cut time.
CO2 lasers have been used for sheet metal cutting since the 1970s and have developed greatly over the years, dominating the industry. If youre looking to mark organic materials like textiles, wood, or cardboard, a CO2 laser is the best choice. Fiber lasers, because of their wavelength, on their own are a Class 4. However, even with CO2 lasers, particularly for thicker sheets, two cut paths are required as with a fiber laser. lasers means for all sheet thicknesses they are able to achieve a smoother cut edge than a fiber, and the difference can become more pronounced as the sheet thickness increases. Finish: CO2 Lasers generally produce better edge quality on plate stainless and aluminum workpieces. Posted By: Southern Fabricating Machinery Sales | Posted On: March 10, 2021. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO. lasers use bend mirrors contained within bellows (sometimes filled with nitrogen) to deliver the beam to the cutting head. However, if small holes/fine features are required, a laser is preferable. The most common cause of misalignment is a collision between the cutting head and a tipped part and can happen for both CO, Misalignment is both more complicated and time consuming to correct on CO. lasers due to the nature of the beam delivery system which normally contains at least three mirrors. For the best cut results, two passes are required: the first to melt the plastic coating and a second to complete the cut. than fiber lasers, CO2 lasers experience higher levels of variation in the quality and output of the laser. If you only need to cut thicker materials, a CO2 laser may be a better option due to faster piercing and faster cutting speeds while producing a smoother surface finish. lasers have been used in the pharmaceutical industry, food production, the manufacturing of electronic components, fabric cutting and cutting building materials. The heat of the laser often causes the mirrors to distort, reducing the power supplied to the cutting head leading to the misalignment of the laser beam. A plasma machine will be able to cut 10 mm mild steel quicker and produce a smoother cut edge. Saquib Ansari Managing Director Esprit Automation Ltd. Esprit Automation is a leading manufacturer of CNC laser, plasma and flame cutting machines in the UK. In conclusion, on average a fiber laser will use approximately 40% more nitrogen per hour than a CO2 laser when cutting stainless steel and approximately 20% more oxygen when cutting mild steel. Innovative feature to reduce idle time on a Fiber Laser. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. Fiber Laser, which is better? Fiber lasers are significantly faster at cutting thin sheets (< 8 mm) than CO2 lasers, particularly when cutting stainless steel. Known Technology: As CO2 Lasers have been around for some 30+ Years the technology, and thus the results are quite predictable. Fiber lasers are significantly better at cutting highly reflective metals such as copper and brass. Increasing the power of the laser source by just 2kW can increase cutting speeds by 2-3 times for thin sheets. The two main consumables of a fiber laser are the nozzle (the same applies for CO2 lasers) and the protective window. This obviously increases the overall cut time.  If you need to cut thicker materials, its best to go with CO2 lasers. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. The acquisition cost of any laser machine depends on a wide range of factors such as: An industrial, second hand CO2 laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. 1390 Read on to find out which cutting technology will best suit your business. Ultimately it comes down to the material you are cutting type and thickness of it. A clue to the answer is the realization that most manufacturers offer BOTH CO2 and Fiber Laser Technologies in their machinery product offering. Fiber lasers have a monolithic configuration whereby the laser beam is delivered to the cutting head via a fiber optic cable.
If you need to cut thicker materials, its best to go with CO2 lasers. However, the speed advantage is tiny in comparison to thinner sheets. The acquisition cost of any laser machine depends on a wide range of factors such as: An industrial, second hand CO2 laser system can cost around 150,000 upwards. The footprint of the machine will largely depend on the size of the cutting bed and shuttle tables used. 1390 Read on to find out which cutting technology will best suit your business. Ultimately it comes down to the material you are cutting type and thickness of it. A clue to the answer is the realization that most manufacturers offer BOTH CO2 and Fiber Laser Technologies in their machinery product offering. Fiber lasers have a monolithic configuration whereby the laser beam is delivered to the cutting head via a fiber optic cable.  Table 6: Auxiliary Gas Consumption for different laser cutting technologies. A Fiber Laser is simply a term used for the fiber optic delivery method of bringing the intense and amplified light source to the cutting head of the laser machine. Once the CO2 Resonator has created enough light it is delivered in a different manner then the fiber optic method. Given the beam delivery system is more exposed to the environment (temperature, moisture etc.) While Fiber Laser technology is not far off as of the writing of this article today CO2 is still the leader in this area.
Table 6: Auxiliary Gas Consumption for different laser cutting technologies. A Fiber Laser is simply a term used for the fiber optic delivery method of bringing the intense and amplified light source to the cutting head of the laser machine. Once the CO2 Resonator has created enough light it is delivered in a different manner then the fiber optic method. Given the beam delivery system is more exposed to the environment (temperature, moisture etc.) While Fiber Laser technology is not far off as of the writing of this article today CO2 is still the leader in this area.